前節まででシェーダにデータを与える基本的な方法については終わりです。
この節では発展編として、実用的な3DCGの処理の話をしていきます。Vulkanというよりは3DCG一般における数学とアルゴリズムの話になります。
線形代数学の知識を必要とする行列などの数式が出てきますが、よく分からなければ数式を読み飛ばして実装だけ読んでも構いません。
MVP 行列
3Dモデルを2Dの画面に表示するにあたって避けて通れないことがあります。 それはコンピュータ内の三次元世界に存在する頂点の座標を二次元である画面上の座標に変換することです。
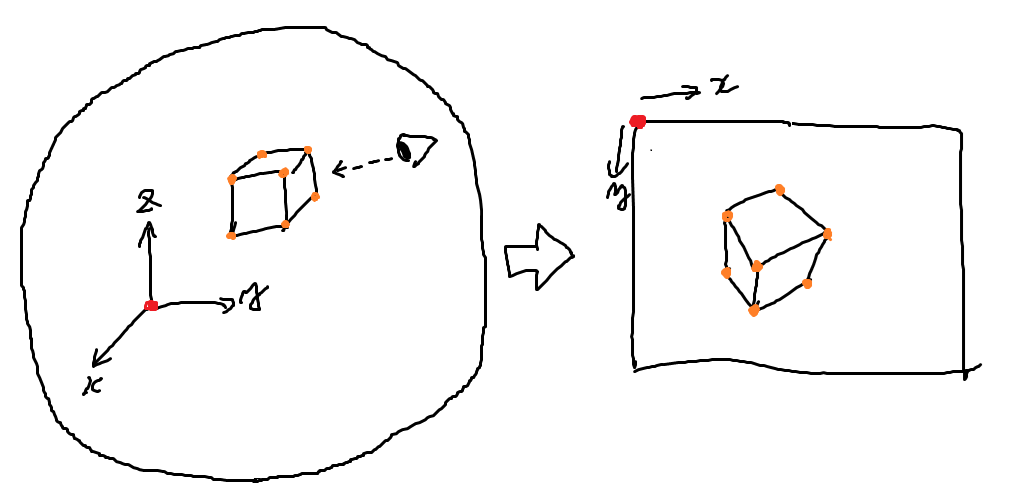
プログラムが初めに持っているのは
- モデルの頂点集合のデータ(各頂点の3次元座標)
- モデルの配置データ(座標、向き)
- カメラ(視点)の位置(座標、向き)
のみなので、これらの値から2次元の画面上の座標を導く必要があります。今まで色々いじくってきた頂点シェーダというのは、ほぼほぼこの計算のために存在するものです。
これから計算式を説明していくのですが、結果から言ってしまえば元の座標ベクトルにある行列をかける計算に集約されます。
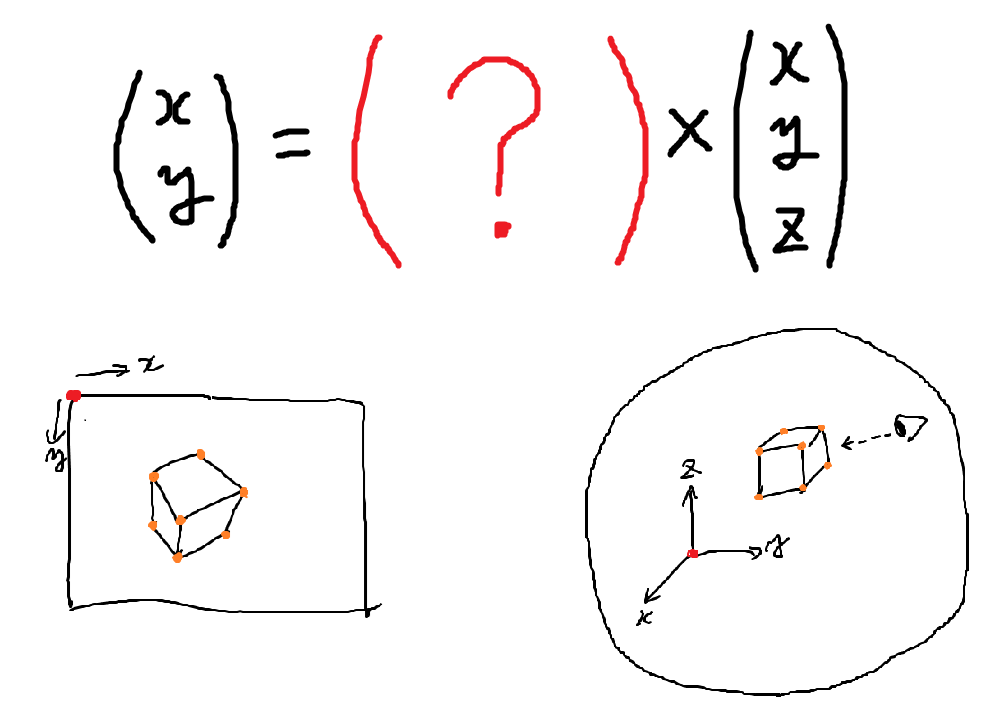
この行列がMVP行列と呼ばれています。
(注): 行列が良くわからない人は「ベクトルを変換する関数の一種」と考えてくれれば十分だと思います。「ベクトルに行列を掛ける」=「ベクトルをある種の関数で変換する」くらいのノリで OK です。
プログラムの概観
実際のプログラムとしてはおおよそ以下のような形になります。
- モデルの頂点データをGPUに渡す(頂点バッファ)
- MVP行列の値をCPU側で算出する
- MVP行列の値をGPUに渡す(デスクリプタ または プッシュ定数)
- MVP行列をかける演算をGPU側で行って頂点座標を変換する
GPUは大量の並列計算が得意なので、3Dモデルを構成する大量の頂点にそれぞれ同じ行列をかけるといった計算は得意分野です。(というより、そのために生まれたのが今のGPUです。)
MVP行列は以下の3つの行列で表されます。
- モデル行列
- ビュー行列
- プロジェクション行列
MVPというのはこの頭文字です。 数式で表すと以下のようになります。
$$P_s = P\times V\times M \times P_m$$
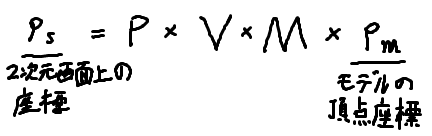
順に見て行きましょう。
モデル行列
これはモデルの移動、回転などを表す行列です。 端的に言えば、モデルを世界に配置するための行列です。
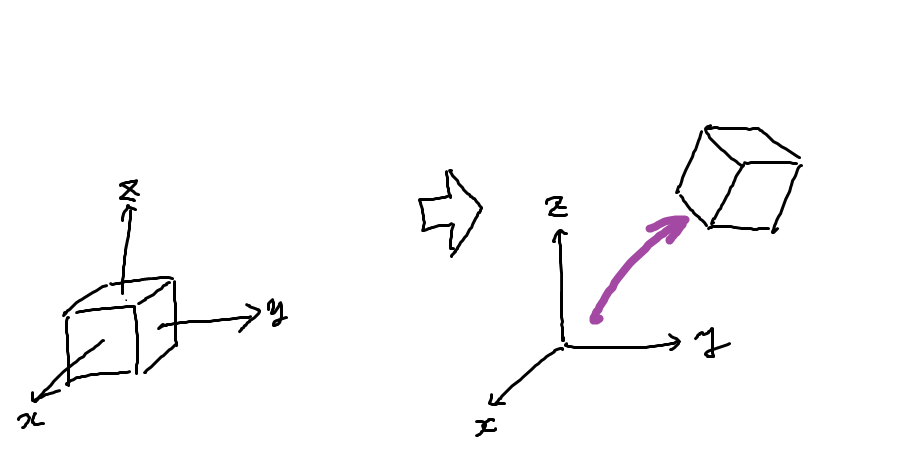
これを使うことで3Dモデルを世界の色々な位置に配置・移動させることができます。
例えばゲームなどでキャラが動き回る場合はキャラのモデルデータを変えず、モデル行列を順次変えていくことでその動きを表します。
ローカル座標・ワールド座標
少し3DCG用語の解説になりますが、元々の3Dモデルの中における座標をローカル座標、3Dモデルの配置される世界における座標をワールド座標と呼びます。
3DCGにおいてはしばしば使われる用語なので、覚えておくと良いかもしれません。 モデル行列は「ローカル座標をワールド座標に変換する行列」ということになるでしょう。
拡縮・回転・平行移動
モデル行列の中身はさらに拡大縮小、回転、平行移動に分けることが出来ます。
平行移動した後に回転や拡大縮小をすると大変なので、多くの場合は拡大縮小 → 回転 → 平行移動という順番で行われます。
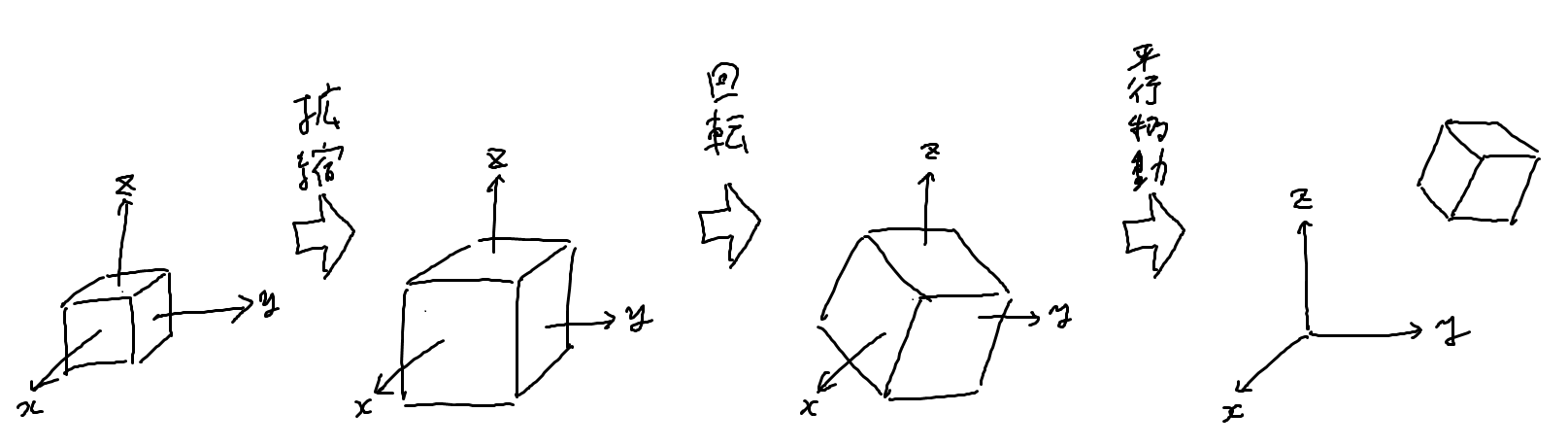
拡大縮小
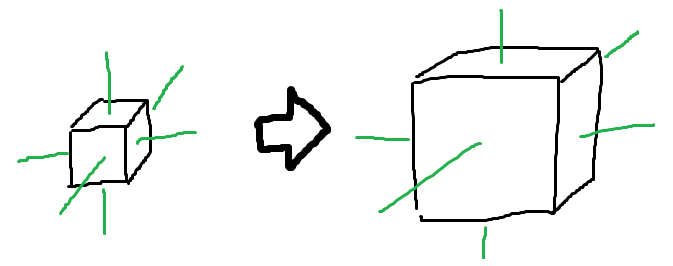
$$ M_S = \begin{pmatrix} s & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & s & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & s & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$s_x: 拡大率$$
各軸方向で拡大率が違う場合は以下のようになります。
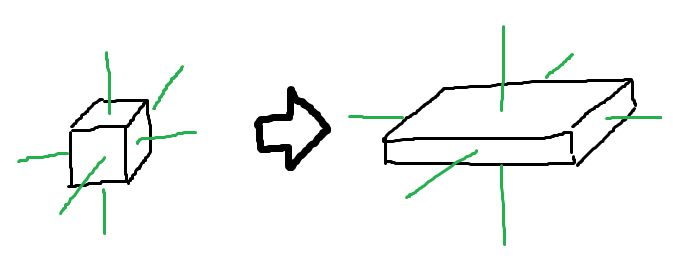
$$ M_S = \begin{pmatrix} s_x & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & s_y & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & s_z & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$s_x: ローカル座標系X軸方向の拡大率$$
$$s_y: ローカル座標系Y軸方向の拡大率$$
$$s_z: ローカル座標系Z軸方向の拡大率$$
回転
そもそも3次元における回転はどのように表すべきでしょうか?2次元なら「時計回りに30度」などと表現できますが、3次元だとそれでは不十分です。
分かりやすく明確なのは回転軸の向きとその軸周りに何度回るかの組み合わせで表現することです。

回転行列は以下のように表せることが知られています。(参考)
$$ M_R = \begin{pmatrix} n_x^2(1-\cos\theta)+\cos \theta & n_x n_y(1-\cos\theta)-n_z\sin \theta & n_x n_z(1-\cos\theta)+n_y\sin \theta & 0 \\ n_y n_x(1-\cos\theta)+n_z\sin \theta & n_y^2(1-\cos\theta)+\cos \theta & n_y n_z(1-\cos\theta)-n_x\sin \theta & 0 \\ n_z n_x(1-\cos\theta)-n_y\sin \theta & n_z n_y(1-\cos\theta)+n_x\sin \theta & n_z^2(1-\cos\theta)+\cos \theta & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$(n_x, n_y, n_z): 回転軸の向きの単位ベクトル$$
$$\theta: 軸周りに回転する角度$$
平行移動
大きさや向きを決めた後で位置を設定します。
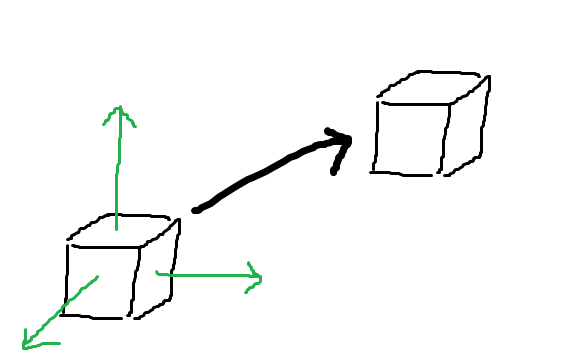
$$ M_T = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & m_x \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & m_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & m_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$m_x: ワールド座標系X軸方向の移動$$
$$m_y: ワールド座標系Y軸方向の移動$$
$$m_z: ワールド座標系Z軸方向の移動$$
モデル行列の値
$$M=M_T \times M_R \times M_S$$
拡大縮小 → 回転 → 平行移動 の順となっていることに注意してください。
(補足)同次変換行列
3次元なのに3x3行列ではなく4x4行列を使って変換を表している理由を説明します。
まず、単純な行列の掛け算は線形写像なので、いわゆる切片を持てません。座標0は座標0にしか写らないという特性があります。 すると拡大縮小や回転は出来るのですが、平行移動ができないという問題があります。
これは変換式の$$\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}$$ を $$\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}+\mathbf{b}$$ということにすれば解決はするのですが、できれば切片\(\mathbf{b}\)の情報もひとつの行列にまとめられた方が便利です。
そこで以下のような数学的工夫をします。
$$\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}+\mathbf{b}$$ $$=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}+\mathbf{b}\cdot 1$$ $$=\begin{pmatrix}\mathbf{A} & \mathbf{b}\end{pmatrix}\begin{pmatrix}\mathbf{x} \\ 1\end{pmatrix}=\mathbf{A'}\mathbf{x'}$$
こうすると3x4行列\(\mathbf{A'}\)で平行移動も含めた変換を表すことができます。また3次元ベクトル\(\mathbf{x}\)は、切片を表すための1が付いた4次元ベクトル\(\mathbf{x'}\)になります。
平行移動を含む変換をいくつも連鎖させることを考えると、変換後の\(\mathbf{y}\)も1が付いた4次元ベクトル\(\mathbf{y'}\)である方が都合が良さそうですね。ということで、以下のような4x4の行列がよく使われます。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} A_{11} & A_{12} & A_{13} & b_1 \\ A_{21} & A_{22} & A_{23} & b_2 \\ A_{31} & A_{32} & A_{33} & b_3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
このような変換行列を同次変換行列、1次元拡張されたベクトルを同次座標ベクトルなどと呼びます。
コンピュータグラフィックス以外の分野でも使われる数学的テクニックです。
(補足)クォータニオン
ここでは3次元の回転を考えるにあたって回転行列しか紹介しませんでしたが、別の便利な数学的道具としてクォータニオンというものがあります。ハミルトンの四元数とも呼ばれます。 高校数学では実数を2次元に拡張した複素数というものを学びますが、それをさらに4次元に拡張したものです。
4つの数だけで回転状態を明確に扱えるほか、回転の線形補間(slerp)の計算に都合が良いという利点があります。
そのため最終的な計算には回転行列を用いますが、状態の保持にはクォータニオンを用いることが多いです。後の章で扱うことになるかと思います。
ビュー行列
これはカメラの位置・姿勢情報を反映させるための行列です。 ビュー行列をかけるとカメラの位置を原点、カメラの向きを座標軸とする座標系での位置が求められます。
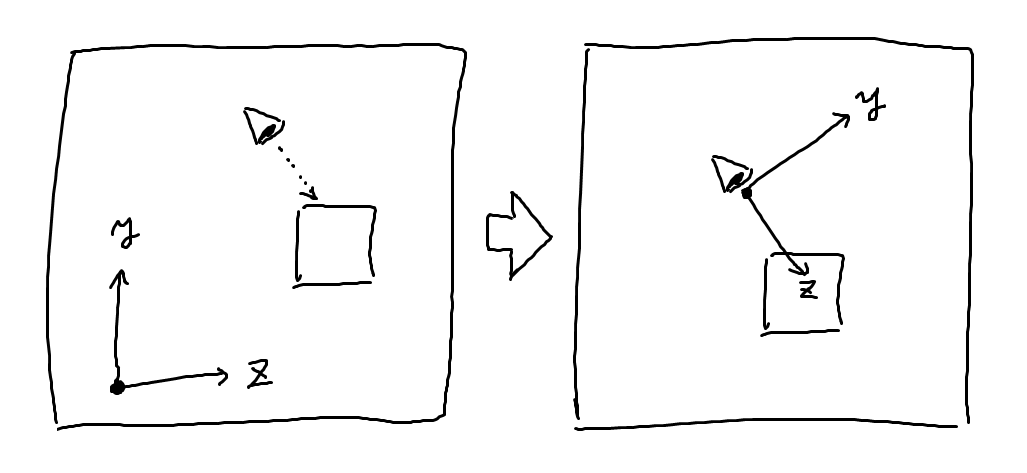
これによって、例えばカメラの目の前にあるものは座標原点の目の前になり、カメラを右に傾ければ全てのものは左に傾きます。
ワールド座標・カメラ座標
3Dモデルが配置された世界の座標をワールド座標と呼んでいたのに対し、カメラを原点とした座標系をカメラ座標と呼びます。
ビュー行列は「ワールド座標をカメラ座標に変換する行列」ということになるでしょう。
X,Y,Z軸の対応
理屈で言えば、カメラ座標のどの向きにX,Y,Z軸を対応させても大した違いはないのですが、 Vulkanほか大抵のグラフィックAPIだと慣例的にX軸を横向き、Y軸を縦向き、Z軸を奥行方向に取ります。
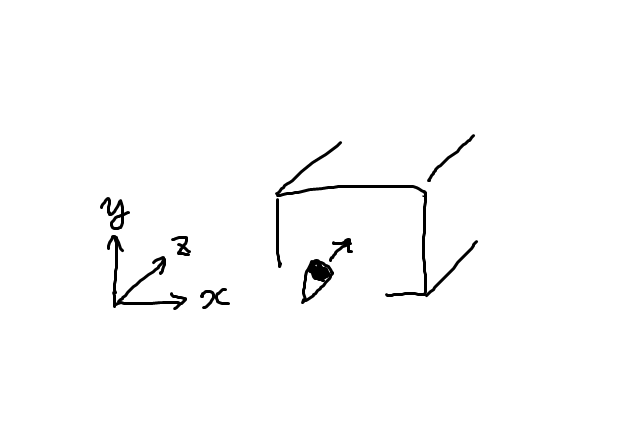
なお「X軸正方向は右か左か」「Y軸正方向は上か下か」「Z軸正方向は奥か手前か」にはAPIでブレがあります。VulkanではX軸:右、Y軸:下、Z軸:奥です。
では、ビュー行列の値を計算してみましょう。
カメラ位置を原点とする
カメラ位置が原点となるような変換を考えてみましょう。カメラ位置が\((c_x,c_y,c_z)\)とした場合、表示されている全てのものを\((-c_x, -c_y, -c_z)\)だけ平行移動させる必要があります。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & -c_x \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -c_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
これで全てのものがカメラを基準とした位置に移動します。
座標軸をカメラの向きに合わせる
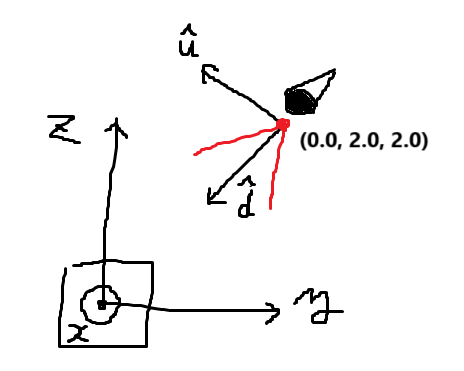
次にカメラの向いている方を変換後のZ軸、カメラの縦方向を変換後のY軸とするような変換を考えます。それぞれの単位ベクトルを求めれば基底の変換の要領で座標変換ができるはずです。
カメラの向きを表すベクトルを\(\mathbf{d}\)、上方向を表すベクトルを\(\mathbf{u}\)(ただし\(\mathbf{d} \perp \mathbf{u}\))とすれば、これらはそれぞれ変換後のZ軸・Y軸の単位ベクトルとして使えます。
$$\hat{\mathbf{y}}' = -\hat{\mathbf{u}}$$ $$\hat{\mathbf{z}}' = \hat{\mathbf{d}}$$
そうすると右手系であれば、変換後のX軸は外積を使って\(\hat{\mathbf{x}}'=\hat{\mathbf{y}}'\times \hat{\mathbf{z}}'\)と表せます。これらを用いればカメラの向きに合わせる変換行列が作れます。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} \hat{x}'_x & \hat{x}'_y & \hat{x}'_z & 0 \\ \hat{y}'_x & \hat{y}'_y & \hat{y}'_z & 0 \\ \hat{z}'_x & \hat{z}'_y & \hat{z}'_z & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} \hat{u}_z \hat{d}_y-\hat{u}_y \hat{d}_z & \hat{u}_x \hat{d}_z-\hat{u}_z \hat{d}_x & \hat{u}_y \hat{d}_x-\hat{u}_x \hat{d}_y & 0 \\ -\hat{u}_x & -\hat{u}_y & -\hat{u}_z & 0 \\ \hat{d}_x & \hat{d}_y & \hat{d}_z & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
ビュー行列の値
上記の2行列の積として表すことができます。
$$ V= \begin{pmatrix} \hat{u}_z \hat{d}_y-\hat{u}_y \hat{d}_z & \hat{u}_x \hat{d}_z-\hat{u}_z \hat{d}_x & \hat{u}_y \hat{d}_x-\hat{u}_x \hat{d}_y & 0 \\ -\hat{u}_x & -\hat{u}_y & -\hat{u}_z & 0 \\ \hat{d}_x & \hat{d}_y & \hat{d}_z & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & -c_x \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -c_z \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
これでワールド座標からカメラ座標への変換ができます。
(補足)平行投影
カメラ座標でのXY座標をそのまま画面のXY座標と対応させた場合どうなるでしょうか。 少し考えてみると分かりますが、近くのものも遠いものも全く同じ大きさに見えることになります。 このような描画方法は平行投影と呼ばれており、設計図の図面や、いわゆるクォータービューのゲームなどで使われています。
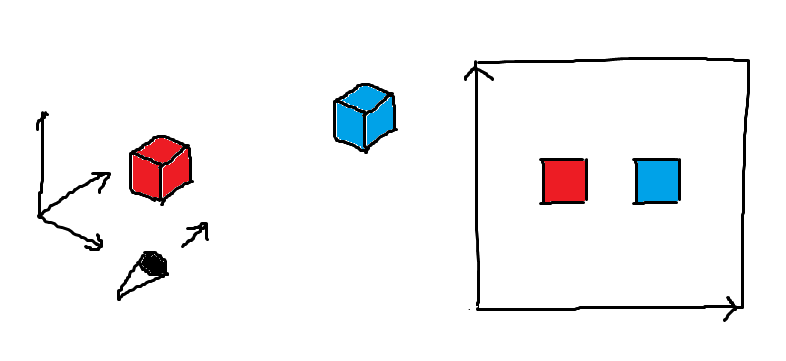
一般的な3DCGのように遠近感を付けるためには、次のプロジェクション行列(射影行列)による変換が必要になります。
プロジェクション行列
これはカメラ座標から最終的な画面上の座標を計算するための行列です。主に3つの役割があります。
- パースをつける
- 画面縦横比への対応
- 右手・左手座標系変換(必要な場合のみ)
パースをつける
プロジェクション行列を掛けることによって遠くのものが小さく、近くのものが大きく見えるようになります。
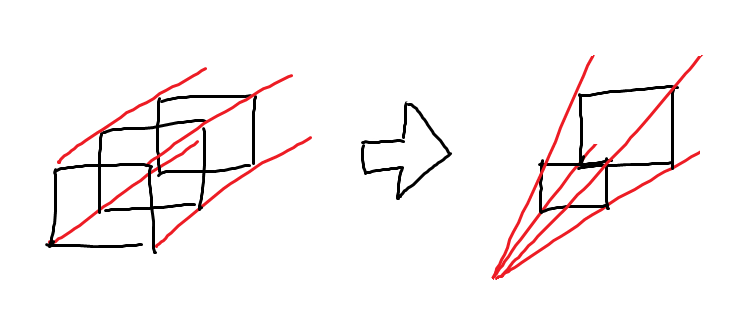
上の図における赤い線は、画面の4隅に対応します。近くにあるものは画面上で大きく映り、遠くにあるものは小さく映ることが分かるかと思います。
w除算
遠くに行くほど小さく見えるような座標変換は、具体的な形としてはZ軸の値に反比例してX,Y軸の値を小さくするような形になります。
$$x' = ax / z$$ $$y' = by / z$$
しかし線形代数の知識がある人であれば、線形写像ではこのような変換は不可能であることに気付かれたのではないでしょうか。一体どうするのでしょう。
実は、現代のGPUではw除算(perspective division)と呼ばれる機能が暗黙的に付いています。これは本来4x4行列を4次元ベクトルにかけたら
$$ \begin{pmatrix}x' \\ y' \\ z' \\ w' \end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} A_{11} & A_{12} & A_{13} & A_{14} \\ A_{21} & A_{22} & A_{23} & A_{24} \\ A_{31} & A_{32} & A_{33} & A_{34} \\ A_{41} & A_{42} & A_{43} & A_{44} \\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix}x \\ y \\ z \\ w \end{pmatrix} =\begin{pmatrix}A_{11} x + A_{12} y + A_{13} z + A_{14} w \\ A_{21} x + A_{22} y + A_{23} z + A_{24} w \\ A_{31} x + A_{32} y + A_{33} z + A_{34} w \\ A_{41} x + A_{42} y + A_{43} z + A_{44} w\end{pmatrix} $$
となるべきところ、
$$ \begin{pmatrix}x'' \\ y'' \\ z'' \\ w'' \end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix}x'/w' \\ y'/w' \\ z'/w' \\ w'/w' \end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix}(A_{11} x + A_{12} y + A_{13} z + A_{14}) / (A_{41} x + A_{42} y + A_{43} z + A_{44} w) \\ (A_{21} x + A_{22} y + A_{23} z + A_{24} w) / (A_{41} x + A_{42} y + A_{43} z + A_{44} w) \\ (A_{31} x + A_{32} y + A_{33} z + A_{34} w) / (A_{41} x + A_{42} y + A_{43} z + A_{44} w) \\ 1\end{pmatrix} $$
となる機能です。早い話が4x4行列をかけると、普通に行列の掛け算を行った後に4番目の値wで全体が割られます。これをw除算と呼びます。これはGPUの仕様です。そういう風に出来ています。 普通の線形代数の知識で見ると気持ち悪いかもしれませんが、こうなると都合が良いのでこうされています。
これを利用することでパースをかけることが出来ます。
視錐台
プロジェクション行列による変換を考える際に有用なのが「視錐台」という概念です。 これはカメラに収まる範囲を表す仮想的な図形です。
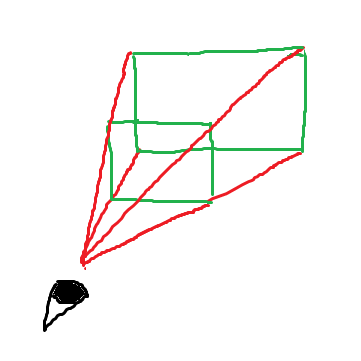
Blenderのような3DCGソフトを使ったことがある人は、UIの一部としても見たことがあるのではないでしょうか。
図の赤で書いた線は画面の四隅に対応しており、緑の線で表した面はクリッピング面と呼ばれます。
カメラ画角
視錐台の決め方には、カメラの画角(視野角)による自由度があります。
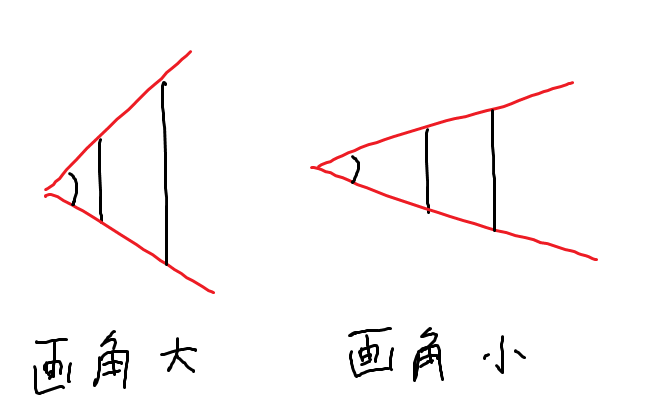
画面の上下端、あるいは左右端がどれくらいの角度の線に対応するかということです。これは好み次第ということになるでしょう。
パースをつける
3章5節において、画面の左右の端がx=±1.0、画面の上下の端がy=±1.0に対応することを説明しました。 ということは、
- 視錐台の左の面がx=-1.0
- 視錐台の右の面がx=+1.0
- 視錐台の上の面がy=-1.0
- 視錐台の下の面がy=+1.0
に対応する必要があります。
例えば、以下のような視錐台で描画するとしましょう。
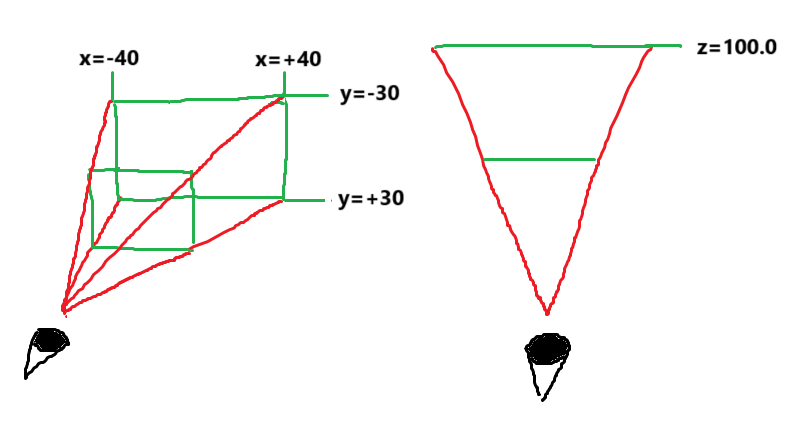
距離100.0においてx=±40.0、y=±30.0が画面の端に対応します。ということは、
$$x'=\frac{100.0}{40.0} \cdot \frac{x}{z}$$
$$y'=\frac{100.0}{30.0} \cdot \frac{y}{z}$$
という変換になる必要があるでしょう。
w除算を踏まえると、パースをつけるための行列は以下のようになります。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} \frac{100.0}{40.0} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \frac{100.0}{30.0} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} $$
一般的にはこうです。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} k_x & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & k_y & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$k_x: X方向の視野角の傾き$$
$$k_y: Y方向の視野角の傾き$$
\(k_x\)や\(k_y\)の値はカメラ画角の好み次第なので自由に設定して良いですが、比については画面の縦横比に合わせる必要があります。そうでないと表示が歪んでしまいます。
$$k_x : k_y = W : H$$ $$W: 画面の横幅$$ $$H: 画面の横幅$$
ところで上記の行列ですが、上から3行目が \(0\ 0\ 1\ 0\) ではなく \(0\ 0\ 0\ 1\) となっています。これはなぜでしょうか。
これは、\(0\ 0\ 1\ 0\)としてしまうと \(z'=z/z=1\) になってZ軸の情報が失われてしまうためです。\(0\ 0\ 0\ 1\)としておけば \(z'=1/z\) となるため、逆数にはなりますが一応情報が保たれます。
Z軸の値は画面上の位置には影響しませんが、正しい描画には奥行きの情報が必要なため、情報を保つ必要があります。
- 前後関係を正しく描画する(7章で解説)
- クリッピングに用いる
主にこの2つの利用目的があるため、奥行の情報が失われては困るのです。
クリッピング面
さて、プロジェクション行列を計算するにあたってもう1つ考えることがあります。それは何かというと、視錐台の話の際に説明を飛ばしたクリッピング面です。これは何かと言うと、遠すぎるものや近すぎるものは描画しないという話です。3Dゲームをプレイしたことのある人は身に覚えがあるのではないでしょうか。
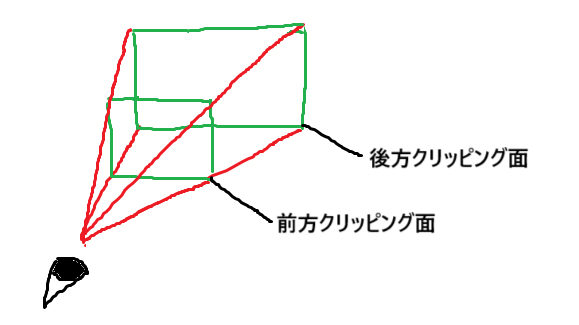
カメラに近い方を前方クリッピング面、カメラから遠い方を後方クリッピング面と呼び、それに挟まれた空間のものだけを描画します。
実はVulkanではZ軸でのクリッピングがデフォルトでオンになっており、Z軸の値が[0.0, 1.0]の範囲をはみ出す箇所は自動的に描画を飛ばされます。 最終的なZ軸の値は画面上の位置には影響しませんが、クリッピングに影響するのです。
試しに頂点シェーダの出力するZ座標を変えてみれば、描画されなくなる(クリッピングされる)ことを確認できるでしょう。
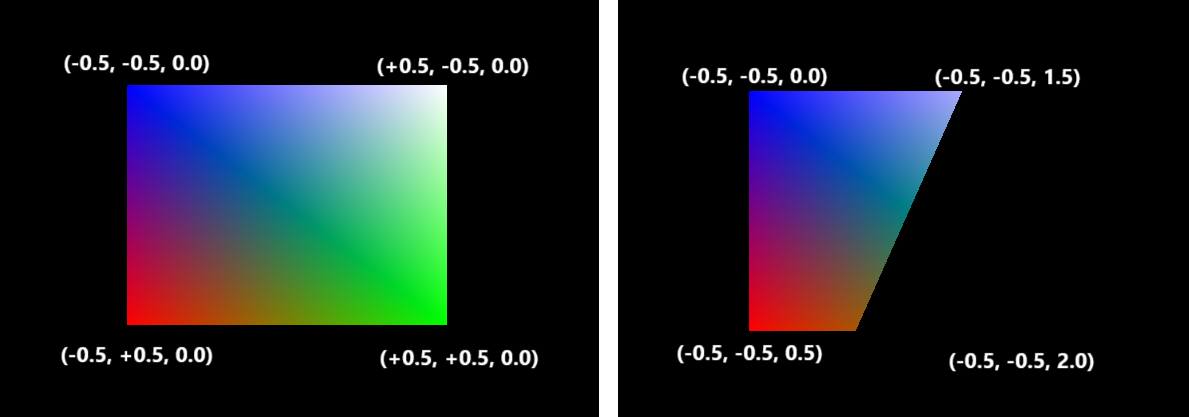
0.0~1.0の範囲をはみ出したピクセルは描画されていない事がわかります。
つまり、もしワールド座標系で[5.0, 100.0]の範囲だけを描画したいとしたら、[5.0, 100.0]を[0.0, 1.0]に対応させるという変換を行う必要があります。 この計算式を考えてみましょう。
Z軸の変換
前方クリッピング面までの距離を \(N\) 、後方クリッピング面までの距離を \(F\) としましょう。
- \(z=N\) のとき \(z'=0.0\)
- \(z=F\) のとき \(z'=1.0\)
となるような変換を考えます。\(z\) は \(1/z\) に変換されているので、 \(1/z\) に対する1次関数でなければなりません。結論から言うとこうなります。
$$z'= \left( \frac{1}{N}-\frac{1}{z} \right) / \left(\frac{1}{N}-\frac{1}{F} \right)$$
$$=-\frac{NF}{F-N} \cdot \frac{1}{z} + \frac{F}{F-N}$$
$$N: 前方クリッピング面までの距離$$
$$F: 後方クリッピング面までの距離$$
行列にすればこうです。
$$ \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -\frac{NF}{F-N} & \frac{F}{F-N} \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
パースをかけるための行列と組み合わせれば、プロジェクション行列の完成になります。
$$ P= \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -\frac{NF}{F-N} & \frac{F}{F-N} \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \times \begin{pmatrix} k_x & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & k_y & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} $$
$$ =\begin{pmatrix} k_x & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & k_y & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \frac{F}{F-N} & -\frac{NF}{F-N} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} $$
実装
実際にプログラムを書いて本格的な3D描画を試してみましょう。
行列を表す構造体の定義
計算の補助として以下のような構造体と演算子オーバーロードを作っておきましょう。
struct Mat4x4 {
float v[4][4];
};
Mat4x4 operator*(const Mat4x4 &a, const Mat4x4 &b) {
Mat4x4 c = {};
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
c.v[i][j] += a.v[k][j] * b.v[i][k];
return c;
}
注意点ですが、行列の値はメモリ上では以下のような順序になります。プログラムの上だと縦横逆に見えることに注意しましょう。
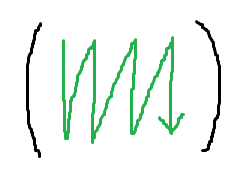
モデル行列の計算
Mat4x4 scaleMatrix(float scale) {
return Mat4x4{{
{scale, 0, 0, 0},
{0, scale, 0, 0},
{0, 0, scale, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
}
Mat4x4 rotationMatrix(Vec3 n, float theta) {
float c = cos(theta);
float s = sin(theta);
float nc = 1 - c;
return Mat4x4{{
{n.x * n.x * nc + c, n.x * n.y * nc + n.z * s, n.x * n.z * nc - n.y * s, 0},
{n.y * n.x * nc - n.z * s, n.y * n.y * nc + c, n.y * n.z * nc + n.x * s, 0},
{n.z * n.x * nc + n.y * s, n.z * n.y * nc - n.x * s, n.z * n.z * nc + c, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
}
Mat4x4 translationMatrix(Vec3 v) {
return Mat4x4{{
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{v.x, v.y, v.z, 1},
}};
}
ビュー行列の計算
Mat4x4 viewMatrix(Vec3 cameraPos, Vec3 dir, Vec3 up) {
const auto cameraShift =
Mat4x4{{
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{-cameraPos.x, -cameraPos.y, -cameraPos.z, 1},
}};
const auto cameraRotation =
Mat4x4{{
{up.z * dir.y - up.y * dir.z, -up.x, dir.x, 0},
{up.x * dir.z - up.z * dir.x, -up.y, dir.y, 0},
{up.y * dir.x - up.x * dir.y, -up.z, dir.z, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
return cameraRotation * cameraShift;
}
プロジェクション行列の計算
Mat4x4 projectionMatrix(float angle_y, float ratio, float near, float far) {
float ky = tan(angle_y);
float kx = ky * ratio;
return Mat4x4{{
{kx, 0, 0, 0},
{0, ky, 0, 0},
{0, 0, far/(far-near), 1},
{0, 0, -near*far/(far-near), 0}
}};
}
MVP行列
適当にモデルとカメラを配置してみます。
auto model = translationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}) * rotationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f}, 0.5f) * scaleMatrix(1.0f);
auto view = viewMatrix({0.0f, 2.0f, 2.0f}, {0.0f, -0.707f, -0.707f}, {0.0f, -0.707f, +0.707f});
auto proj = projectionMatrix(3.14f / 3, screenWidth / screenHeight, 0.1f, 100.0f);
auto mvpMatrix = proj * view * model;
行列をシェーダに渡す
別にプッシュ定数でもデスクリプタ+ユニフォームバッファでも良いのですが、ここでは前節で解説したプッシュ定数を利用してみます。
struct SceneData {
Mat4x4 mvpMatrix;
};
vk::PipelineLayoutCreateInfo layoutCreateInfo;
vk::PushConstantRange pushConstantRange[1];
pushConstantRange[0].offset = 0;
pushConstantRange[0].size = sizeof(SceneData);
pushConstantRange[0].stageFlags = vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eVertex;
layoutCreateInfo.pPushConstantRanges = pushConstantRange;
layoutCreateInfo.pushConstantRangeCount = 1;
sceneData.mvpMatrix = mvpMatrix;
cmdBufs[0]->pushConstants(pipelineLayout.get(), vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eVertex, 0, sizeof(SceneData), &sceneData);
頂点シェーダ
#version 450
#extension GL_ARB_separate_shader_objects : enable
layout(push_constant) uniform SceneData {
mat4 mvpMatrix;
} drawInfo;
layout(location = 0) in vec3 inPos;
layout(location = 1) in vec3 inColor;
layout(location = 0) out vec3 fragmentColor;
void main() {
gl_Position = drawInfo.mvpMatrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0);
fragmentColor = inColor;
}
モデルデータの用意
頂点データの位置情報posを3次元ベクトルにしましょう。
せっかくなので、ただの四角ではなく箱を表示してみます。
struct Vertex {
Vec3 pos;
Vec3 color;
};
std::vector<Vertex> vertices = {
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 0.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 1.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 1.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 0.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 0.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 1.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 1.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 0.0, 0.0}},
};
std::vector<uint16_t> indices = {
0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 5, 4, 6, 4, 5, 7,
4, 3, 0, 3, 4, 7, 1, 6, 2, 6, 1, 5,
7, 1, 3, 1, 7, 5, 6, 0, 2, 0, 6, 4
};
頂点位置が3次元になったので、頂点入力デスクリプションを変更する必要があります。
vk::VertexInputAttributeDescription vertexInputDescription[2];
vertexInputDescription[0].binding = 0;
vertexInputDescription[0].location = 0;
vertexInputDescription[0].format = vk::Format::eR32G32B32Sfloat; // 変更
vertexInputDescription[0].offset = offsetof(Vertex, pos);
vertexInputDescription[1].binding = 0;
vertexInputDescription[1].location = 1;
vertexInputDescription[1].format = vk::Format::eR32G32B32Sfloat;
vertexInputDescription[1].offset = offsetof(Vertex, color);
表示
実行してみましょう。
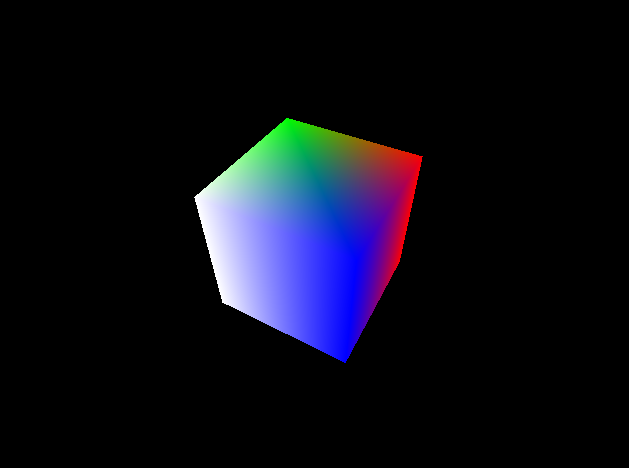
パースの付いた立方体を表示することができました。
(応用)動きを作る
MVP行列を毎フレーム更新すれば動きのあるアニメーションを作ることができます。
1秒に1回転することにしましょう。前フレームからの経過時間を測り、それを使うようにします。
// 追加
#include <chrono>
// 毎フレーム実行
static std::chrono::system_clock::time_point prevTime;
static float rotation = 0.5f;
const auto nowTime = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
const auto delta = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(nowTime - prevTime).count();
rotation += delta * 2 * 3.14f / 1000000;
rotation = fmod(rotation, 2 * 3.14159f);
prevTime = nowTime;
auto model = translationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}) * rotationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f}, rotation) * scaleMatrix(1.0f);
auto view = viewMatrix({0.0f, -2.0f, -2.0f}, {0.0f, +0.707f, +0.707f}, {0.0f, +0.707f, -0.707f});
auto proj = projectionMatrix(3.14f / 3, float(screenHeight) / float(screenWidth), 0.1f, 100.0f);
sceneData.mvpMatrix = proj * view * model;
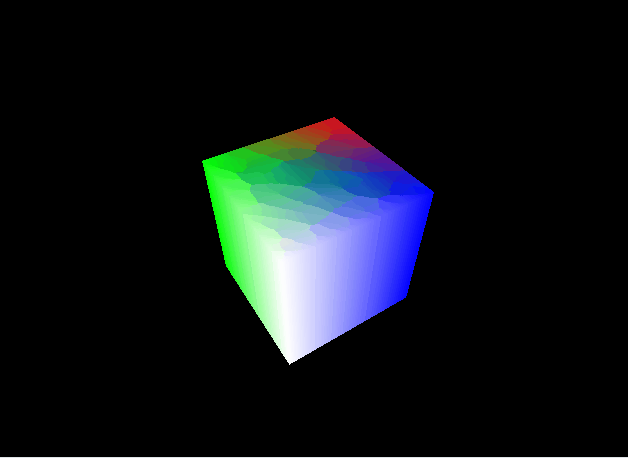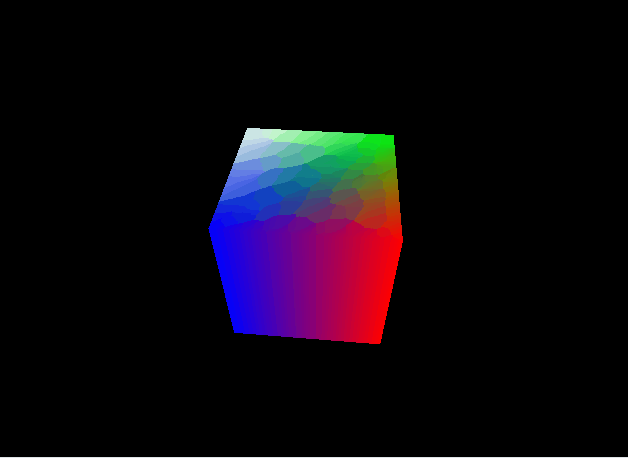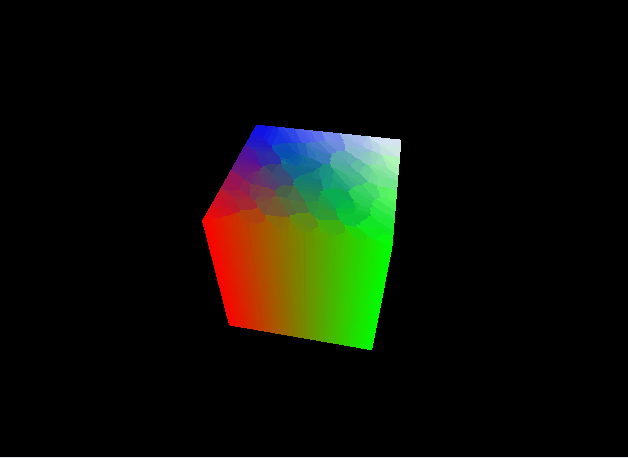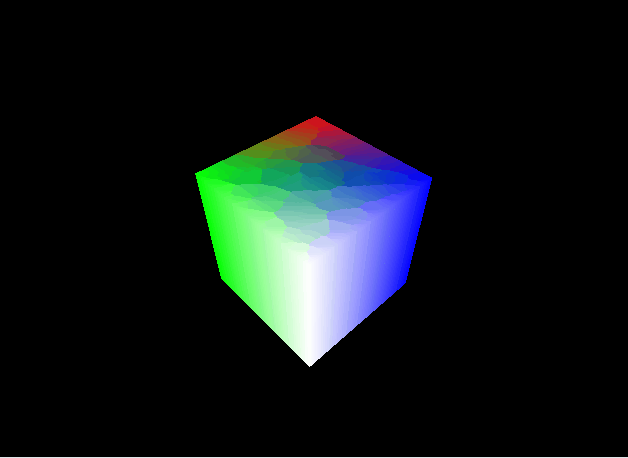
この節ではMVP変換について解説しました。次節ではシェーディングについて解説します。この節のコード
#include <vulkan/vulkan.hpp>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
const uint32_t screenWidth = 640;
const uint32_t screenHeight = 480;
struct Vec2 {
float x, y;
};
struct Vec3 {
float x, y, z;
};
struct Mat4x4 {
float v[4][4];
};
Mat4x4 operator*(const Mat4x4 &a, const Mat4x4 &b) {
Mat4x4 c = {};
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
c.v[i][j] += a.v[k][j] * b.v[i][k];
return c;
}
struct Vertex {
Vec3 pos;
Vec3 color;
};
std::vector<Vertex> vertices = {
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 0.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 1.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 1.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 0.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 0.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{0.0, 1.0, 0.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 1.0, 1.0}},
Vertex{Vec3{-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f}, Vec3{1.0, 0.0, 0.0}},
};
std::vector<uint16_t> indices = {
0, 1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 5, 4, 6, 4, 5, 7,
4, 3, 0, 3, 4, 7, 1, 6, 2, 6, 1, 5,
7, 1, 3, 1, 7, 5, 6, 0, 2, 0, 6, 4
};
struct SceneData {
Mat4x4 mvpMatrix;
};
SceneData sceneData;
Mat4x4 scaleMatrix(float scale) {
return Mat4x4{{
{scale, 0, 0, 0},
{0, scale, 0, 0},
{0, 0, scale, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
}
Mat4x4 rotationMatrix(Vec3 n, float theta) {
float c = cos(theta);
float s = sin(theta);
float nc = 1 - c;
return Mat4x4{{
{n.x * n.x * nc + c, n.x * n.y * nc + n.z * s, n.x * n.z * nc - n.y * s, 0},
{n.y * n.x * nc - n.z * s, n.y * n.y * nc + c, n.y * n.z * nc + n.x * s, 0},
{n.z * n.x * nc + n.y * s, n.z * n.y * nc - n.x * s, n.z * n.z * nc + c, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
}
Mat4x4 translationMatrix(Vec3 v) {
return Mat4x4{{
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{v.x, v.y, v.z, 1},
}};
}
Mat4x4 viewMatrix(Vec3 cameraPos, Vec3 dir, Vec3 up) {
const auto cameraShift =
Mat4x4{{
{1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{-cameraPos.x, -cameraPos.y, -cameraPos.z, 1},
}};
const auto cameraRotation =
Mat4x4{{
{up.z * dir.y - up.y * dir.z, -up.x, dir.x, 0},
{up.x * dir.z - up.z * dir.x, -up.y, dir.y, 0},
{up.y * dir.x - up.x * dir.y, -up.z, dir.z, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
}};
return cameraRotation * cameraShift;
}
Mat4x4 projectionMatrix(float angle_y, float ratio, float near, float far) {
float ky = tan(angle_y);
float kx = ky * ratio;
return Mat4x4{{
{kx, 0, 0, 0},
{0, ky, 0, 0},
{0, 0, far/(far-near), 1},
{0, 0, -near*far/(far-near), 0}
}};
}
int main() {
if (!glfwInit())
return -1;
uint32_t requiredExtensionsCount;
const char **requiredExtensions = glfwGetRequiredInstanceExtensions(&requiredExtensionsCount);
vk::InstanceCreateInfo createInfo;
createInfo.enabledExtensionCount = requiredExtensionsCount;
createInfo.ppEnabledExtensionNames = requiredExtensions;
vk::UniqueInstance instance;
instance = vk::createInstanceUnique(createInfo);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CLIENT_API, GLFW_NO_API);
GLFWwindow *window;
window = glfwCreateWindow(screenWidth, screenHeight, "GLFW Test Window", NULL, NULL);
if (!window) {
const char *err;
glfwGetError(&err);
std::cout << err << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
VkSurfaceKHR c_surface;
auto result = glfwCreateWindowSurface(instance.get(), window, nullptr, &c_surface);
if (result != VK_SUCCESS) {
const char *err;
glfwGetError(&err);
std::cout << err << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
vk::UniqueSurfaceKHR surface{c_surface, instance.get()};
std::vector<vk::PhysicalDevice> physicalDevices = instance->enumeratePhysicalDevices();
vk::PhysicalDevice physicalDevice;
bool existsSuitablePhysicalDevice = false;
uint32_t graphicsQueueFamilyIndex;
for (size_t i = 0; i < physicalDevices.size(); i++) {
std::vector<vk::QueueFamilyProperties> queueProps = physicalDevices[i].getQueueFamilyProperties();
bool existsGraphicsQueue = false;
for (size_t j = 0; j < queueProps.size(); j++) {
if (queueProps[j].queueFlags & vk::QueueFlagBits::eGraphics && physicalDevices[i].getSurfaceSupportKHR(j, surface.get())) {
existsGraphicsQueue = true;
graphicsQueueFamilyIndex = j;
break;
}
}
std::vector<vk::ExtensionProperties> extProps = physicalDevices[i].enumerateDeviceExtensionProperties();
bool supportsSwapchainExtension = false;
for (size_t j = 0; j < extProps.size(); j++) {
if (std::string_view(extProps[j].extensionName.data()) == VK_KHR_SWAPCHAIN_EXTENSION_NAME) {
supportsSwapchainExtension = true;
break;
}
}
if (existsGraphicsQueue && supportsSwapchainExtension) {
physicalDevice = physicalDevices[i];
existsSuitablePhysicalDevice = true;
break;
}
}
if (!existsSuitablePhysicalDevice) {
std::cerr << "使用可能な物理デバイスがありません。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
vk::DeviceCreateInfo devCreateInfo;
auto devRequiredExtensions = {VK_KHR_SWAPCHAIN_EXTENSION_NAME};
devCreateInfo.enabledExtensionCount = devRequiredExtensions.size();
devCreateInfo.ppEnabledExtensionNames = devRequiredExtensions.begin();
vk::DeviceQueueCreateInfo queueCreateInfo[1];
queueCreateInfo[0].queueFamilyIndex = graphicsQueueFamilyIndex;
queueCreateInfo[0].queueCount = 1;
float queuePriorities[1] = {1.0};
queueCreateInfo[0].pQueuePriorities = queuePriorities;
devCreateInfo.pQueueCreateInfos = queueCreateInfo;
devCreateInfo.queueCreateInfoCount = 1;
vk::UniqueDevice device = physicalDevice.createDeviceUnique(devCreateInfo);
vk::Queue graphicsQueue = device->getQueue(graphicsQueueFamilyIndex, 0);
vk::PhysicalDeviceMemoryProperties memProps = physicalDevice.getMemoryProperties();
vk::BufferCreateInfo vertBufferCreateInfo;
vertBufferCreateInfo.size = sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size();
vertBufferCreateInfo.usage = vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eVertexBuffer | vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eTransferDst;
vertBufferCreateInfo.sharingMode = vk::SharingMode::eExclusive;
vk::UniqueBuffer vertexBuf = device->createBufferUnique(vertBufferCreateInfo);
vk::MemoryRequirements vertexBufMemReq = device->getBufferMemoryRequirements(vertexBuf.get());
vk::MemoryAllocateInfo vertexBufMemAllocInfo;
vertexBufMemAllocInfo.allocationSize = vertexBufMemReq.size;
bool suitableMemoryTypeFound = false;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < memProps.memoryTypeCount; i++) {
if (vertexBufMemReq.memoryTypeBits & (1 << i) && (memProps.memoryTypes[i].propertyFlags & vk::MemoryPropertyFlagBits::eDeviceLocal)) {
vertexBufMemAllocInfo.memoryTypeIndex = i;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = true;
break;
}
}
if (!suitableMemoryTypeFound) {
std::cerr << "適切なメモリタイプが存在しません。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
vk::UniqueDeviceMemory vertexBufMemory = device->allocateMemoryUnique(vertexBufMemAllocInfo);
device->bindBufferMemory(vertexBuf.get(), vertexBufMemory.get(), 0);
{
vk::BufferCreateInfo stagingBufferCreateInfo;
stagingBufferCreateInfo.size = sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size();
stagingBufferCreateInfo.usage = vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eTransferSrc;
stagingBufferCreateInfo.sharingMode = vk::SharingMode::eExclusive;
vk::UniqueBuffer stagingBuf = device->createBufferUnique(stagingBufferCreateInfo);
vk::MemoryRequirements stagingBufMemReq = device->getBufferMemoryRequirements(stagingBuf.get());
vk::MemoryAllocateInfo stagingBufMemAllocInfo;
stagingBufMemAllocInfo.allocationSize = stagingBufMemReq.size;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = false;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < memProps.memoryTypeCount; i++) {
if (stagingBufMemReq.memoryTypeBits & (1 << i) && (memProps.memoryTypes[i].propertyFlags & vk::MemoryPropertyFlagBits::eHostVisible)) {
stagingBufMemAllocInfo.memoryTypeIndex = i;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = true;
break;
}
}
if (!suitableMemoryTypeFound) {
std::cerr << "適切なメモリタイプが存在しません。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
vk::UniqueDeviceMemory stagingBufMemory = device->allocateMemoryUnique(stagingBufMemAllocInfo);
device->bindBufferMemory(stagingBuf.get(), stagingBufMemory.get(), 0);
void *pStagingBufMem = device->mapMemory(stagingBufMemory.get(), 0, sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size());
std::memcpy(pStagingBufMem, vertices.data(), sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size());
vk::MappedMemoryRange flushMemoryRange;
flushMemoryRange.memory = stagingBufMemory.get();
flushMemoryRange.offset = 0;
flushMemoryRange.size = sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size();
device->flushMappedMemoryRanges({flushMemoryRange});
device->unmapMemory(stagingBufMemory.get());
vk::CommandPoolCreateInfo tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo;
tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo.queueFamilyIndex = graphicsQueueFamilyIndex;
tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo.flags = vk::CommandPoolCreateFlagBits::eTransient;
vk::UniqueCommandPool tmpCmdPool = device->createCommandPoolUnique(tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo);
vk::CommandBufferAllocateInfo tmpCmdBufAllocInfo;
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.commandPool = tmpCmdPool.get();
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.level = vk::CommandBufferLevel::ePrimary;
std::vector<vk::UniqueCommandBuffer> tmpCmdBufs = device->allocateCommandBuffersUnique(tmpCmdBufAllocInfo);
vk::BufferCopy bufCopy;
bufCopy.srcOffset = 0;
bufCopy.dstOffset = 0;
bufCopy.size = sizeof(Vertex) * vertices.size();
vk::CommandBufferBeginInfo cmdBeginInfo;
cmdBeginInfo.flags = vk::CommandBufferUsageFlagBits::eOneTimeSubmit;
tmpCmdBufs[0]->begin(cmdBeginInfo);
tmpCmdBufs[0]->copyBuffer(stagingBuf.get(), vertexBuf.get(), {bufCopy});
tmpCmdBufs[0]->end();
vk::CommandBuffer submitCmdBuf[1] = {tmpCmdBufs[0].get()};
vk::SubmitInfo submitInfo;
submitInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
submitInfo.pCommandBuffers = submitCmdBuf;
graphicsQueue.submit({submitInfo});
graphicsQueue.waitIdle();
}
vk::BufferCreateInfo indexBufferCreateInfo;
indexBufferCreateInfo.size = sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size();
indexBufferCreateInfo.usage = vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eIndexBuffer | vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eTransferDst;
indexBufferCreateInfo.sharingMode = vk::SharingMode::eExclusive;
vk::UniqueBuffer indexBuf = device->createBufferUnique(indexBufferCreateInfo);
vk::MemoryRequirements indexBufMemReq = device->getBufferMemoryRequirements(indexBuf.get());
vk::MemoryAllocateInfo indexBufMemAllocInfo;
indexBufMemAllocInfo.allocationSize = indexBufMemReq.size;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = false;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < memProps.memoryTypeCount; i++) {
if (indexBufMemReq.memoryTypeBits & (1 << i) && (memProps.memoryTypes[i].propertyFlags & vk::MemoryPropertyFlagBits::eDeviceLocal)) {
indexBufMemAllocInfo.memoryTypeIndex = i;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = true;
break;
}
}
if (!suitableMemoryTypeFound) {
std::cerr << "適切なメモリタイプが存在しません。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
vk::UniqueDeviceMemory indexBufMemory = device->allocateMemoryUnique(indexBufMemAllocInfo);
device->bindBufferMemory(indexBuf.get(), indexBufMemory.get(), 0);
{
vk::BufferCreateInfo stagingBufferCreateInfo;
stagingBufferCreateInfo.size = sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size();
stagingBufferCreateInfo.usage = vk::BufferUsageFlagBits::eTransferSrc;
stagingBufferCreateInfo.sharingMode = vk::SharingMode::eExclusive;
vk::UniqueBuffer stagingBuf = device->createBufferUnique(stagingBufferCreateInfo);
vk::MemoryRequirements stagingBufMemReq = device->getBufferMemoryRequirements(stagingBuf.get());
vk::MemoryAllocateInfo stagingBufMemAllocInfo;
stagingBufMemAllocInfo.allocationSize = stagingBufMemReq.size;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = false;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < memProps.memoryTypeCount; i++) {
if (stagingBufMemReq.memoryTypeBits & (1 << i) && (memProps.memoryTypes[i].propertyFlags & vk::MemoryPropertyFlagBits::eHostVisible)) {
stagingBufMemAllocInfo.memoryTypeIndex = i;
suitableMemoryTypeFound = true;
break;
}
}
if (!suitableMemoryTypeFound) {
std::cerr << "適切なメモリタイプが存在しません。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
vk::UniqueDeviceMemory stagingBufMemory = device->allocateMemoryUnique(stagingBufMemAllocInfo);
device->bindBufferMemory(stagingBuf.get(), stagingBufMemory.get(), 0);
void *pStagingBufMem = device->mapMemory(stagingBufMemory.get(), 0, sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size());
std::memcpy(pStagingBufMem, indices.data(), sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size());
vk::MappedMemoryRange flushMemoryRange;
flushMemoryRange.memory = stagingBufMemory.get();
flushMemoryRange.offset = 0;
flushMemoryRange.size = sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size();
device->flushMappedMemoryRanges({flushMemoryRange});
device->unmapMemory(stagingBufMemory.get());
vk::CommandPoolCreateInfo tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo;
tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo.queueFamilyIndex = graphicsQueueFamilyIndex;
tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo.flags = vk::CommandPoolCreateFlagBits::eTransient;
vk::UniqueCommandPool tmpCmdPool = device->createCommandPoolUnique(tmpCmdPoolCreateInfo);
vk::CommandBufferAllocateInfo tmpCmdBufAllocInfo;
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.commandPool = tmpCmdPool.get();
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
tmpCmdBufAllocInfo.level = vk::CommandBufferLevel::ePrimary;
std::vector<vk::UniqueCommandBuffer> tmpCmdBufs = device->allocateCommandBuffersUnique(tmpCmdBufAllocInfo);
vk::BufferCopy bufCopy;
bufCopy.srcOffset = 0;
bufCopy.dstOffset = 0;
bufCopy.size = sizeof(uint16_t) * indices.size();
vk::CommandBufferBeginInfo cmdBeginInfo;
cmdBeginInfo.flags = vk::CommandBufferUsageFlagBits::eOneTimeSubmit;
tmpCmdBufs[0]->begin(cmdBeginInfo);
tmpCmdBufs[0]->copyBuffer(stagingBuf.get(), indexBuf.get(), {bufCopy});
tmpCmdBufs[0]->end();
vk::CommandBuffer submitCmdBuf[1] = {tmpCmdBufs[0].get()};
vk::SubmitInfo submitInfo;
submitInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
submitInfo.pCommandBuffers = submitCmdBuf;
graphicsQueue.submit({submitInfo});
graphicsQueue.waitIdle();
}
std::vector<vk::SurfaceFormatKHR> surfaceFormats = physicalDevice.getSurfaceFormatsKHR(surface.get());
std::vector<vk::PresentModeKHR> surfacePresentModes = physicalDevice.getSurfacePresentModesKHR(surface.get());
vk::SurfaceFormatKHR swapchainFormat = surfaceFormats[0];
vk::PresentModeKHR swapchainPresentMode = surfacePresentModes[0];
vk::AttachmentDescription attachments[1];
attachments[0].format = swapchainFormat.format;
attachments[0].samples = vk::SampleCountFlagBits::e1;
attachments[0].loadOp = vk::AttachmentLoadOp::eClear;
attachments[0].storeOp = vk::AttachmentStoreOp::eStore;
attachments[0].stencilLoadOp = vk::AttachmentLoadOp::eDontCare;
attachments[0].stencilStoreOp = vk::AttachmentStoreOp::eDontCare;
attachments[0].initialLayout = vk::ImageLayout::eUndefined;
attachments[0].finalLayout = vk::ImageLayout::ePresentSrcKHR;
vk::AttachmentReference subpass0_attachmentRefs[1];
subpass0_attachmentRefs[0].attachment = 0;
subpass0_attachmentRefs[0].layout = vk::ImageLayout::eColorAttachmentOptimal;
vk::SubpassDescription subpasses[1];
subpasses[0].pipelineBindPoint = vk::PipelineBindPoint::eGraphics;
subpasses[0].colorAttachmentCount = 1;
subpasses[0].pColorAttachments = subpass0_attachmentRefs;
vk::RenderPassCreateInfo renderpassCreateInfo;
renderpassCreateInfo.attachmentCount = 1;
renderpassCreateInfo.pAttachments = attachments;
renderpassCreateInfo.subpassCount = 1;
renderpassCreateInfo.pSubpasses = subpasses;
renderpassCreateInfo.dependencyCount = 0;
renderpassCreateInfo.pDependencies = nullptr;
vk::UniqueRenderPass renderpass = device->createRenderPassUnique(renderpassCreateInfo);
vk::Viewport viewports[1];
viewports[0].x = 0.0;
viewports[0].y = 0.0;
viewports[0].minDepth = 0.0;
viewports[0].maxDepth = 1.0;
viewports[0].width = screenWidth;
viewports[0].height = screenHeight;
vk::Rect2D scissors[1];
scissors[0].offset = vk::Offset2D{0, 0};
scissors[0].extent = vk::Extent2D{screenWidth, screenHeight};
vk::PipelineViewportStateCreateInfo viewportState;
viewportState.viewportCount = 1;
viewportState.pViewports = viewports;
viewportState.scissorCount = 1;
viewportState.pScissors = scissors;
vk::VertexInputBindingDescription vertexBindingDescription[1];
vertexBindingDescription[0].binding = 0;
vertexBindingDescription[0].stride = sizeof(Vertex);
vertexBindingDescription[0].inputRate = vk::VertexInputRate::eVertex;
vk::VertexInputAttributeDescription vertexInputDescription[2];
vertexInputDescription[0].binding = 0;
vertexInputDescription[0].location = 0;
vertexInputDescription[0].format = vk::Format::eR32G32Sfloat;
vertexInputDescription[0].offset = offsetof(Vertex, pos);
vertexInputDescription[1].binding = 0;
vertexInputDescription[1].location = 1;
vertexInputDescription[1].format = vk::Format::eR32G32B32Sfloat;
vertexInputDescription[1].offset = offsetof(Vertex, color);
vk::PipelineVertexInputStateCreateInfo vertexInputInfo;
vertexInputInfo.vertexBindingDescriptionCount = std::size(vertexBindingDescription);
vertexInputInfo.pVertexBindingDescriptions = vertexBindingDescription;
vertexInputInfo.vertexAttributeDescriptionCount = std::size(vertexInputDescription);
vertexInputInfo.pVertexAttributeDescriptions = vertexInputDescription;
vk::PipelineInputAssemblyStateCreateInfo inputAssembly;
inputAssembly.topology = vk::PrimitiveTopology::eTriangleList;
inputAssembly.primitiveRestartEnable = false;
vk::PipelineRasterizationStateCreateInfo rasterizer;
rasterizer.depthClampEnable = false;
rasterizer.rasterizerDiscardEnable = false;
rasterizer.polygonMode = vk::PolygonMode::eFill;
rasterizer.lineWidth = 1.0f;
rasterizer.cullMode = vk::CullModeFlagBits::eBack;
rasterizer.frontFace = vk::FrontFace::eClockwise;
rasterizer.depthBiasEnable = false;
vk::PipelineMultisampleStateCreateInfo multisample;
multisample.sampleShadingEnable = false;
multisample.rasterizationSamples = vk::SampleCountFlagBits::e1;
vk::PipelineColorBlendAttachmentState blendattachment[1];
blendattachment[0].colorWriteMask = vk::ColorComponentFlagBits::eA | vk::ColorComponentFlagBits::eR | vk::ColorComponentFlagBits::eG | vk::ColorComponentFlagBits::eB;
blendattachment[0].blendEnable = false;
vk::PipelineColorBlendStateCreateInfo blend;
blend.logicOpEnable = false;
blend.attachmentCount = 1;
blend.pAttachments = blendattachment;
vk::PipelineLayoutCreateInfo layoutCreateInfo;
vk::PushConstantRange pushConstantRange[1];
pushConstantRange[0].offset = 0;
pushConstantRange[0].size = sizeof(SceneData);
pushConstantRange[0].stageFlags = vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eVertex;
layoutCreateInfo.pPushConstantRanges = pushConstantRange;
layoutCreateInfo.pushConstantRangeCount = 1;
vk::UniquePipelineLayout pipelineLayout = device->createPipelineLayoutUnique(layoutCreateInfo);
size_t vertSpvFileSz = std::filesystem::file_size("shader.vert.spv");
std::ifstream vertSpvFile("shader.vert.spv", std::ios_base::binary);
std::vector<char> vertSpvFileData(vertSpvFileSz);
vertSpvFile.read(vertSpvFileData.data(), vertSpvFileSz);
vk::ShaderModuleCreateInfo vertShaderCreateInfo;
vertShaderCreateInfo.codeSize = vertSpvFileSz;
vertShaderCreateInfo.pCode = reinterpret_cast<const uint32_t *>(vertSpvFileData.data());
vk::UniqueShaderModule vertShader = device->createShaderModuleUnique(vertShaderCreateInfo);
size_t fragSpvFileSz = std::filesystem::file_size("shader.frag.spv");
std::ifstream fragSpvFile("shader.frag.spv", std::ios_base::binary);
std::vector<char> fragSpvFileData(fragSpvFileSz);
fragSpvFile.read(fragSpvFileData.data(), fragSpvFileSz);
vk::ShaderModuleCreateInfo fragShaderCreateInfo;
fragShaderCreateInfo.codeSize = fragSpvFileSz;
fragShaderCreateInfo.pCode = reinterpret_cast<const uint32_t *>(fragSpvFileData.data());
vk::UniqueShaderModule fragShader = device->createShaderModuleUnique(fragShaderCreateInfo);
vk::PipelineShaderStageCreateInfo shaderStage[2];
shaderStage[0].stage = vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eVertex;
shaderStage[0].module = vertShader.get();
shaderStage[0].pName = "main";
shaderStage[1].stage = vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eFragment;
shaderStage[1].module = fragShader.get();
shaderStage[1].pName = "main";
vk::GraphicsPipelineCreateInfo pipelineCreateInfo;
pipelineCreateInfo.pViewportState = &viewportState;
pipelineCreateInfo.pVertexInputState = &vertexInputInfo;
pipelineCreateInfo.pInputAssemblyState = &inputAssembly;
pipelineCreateInfo.pRasterizationState = &rasterizer;
pipelineCreateInfo.pMultisampleState = &multisample;
pipelineCreateInfo.pColorBlendState = &blend;
pipelineCreateInfo.layout = pipelineLayout.get();
pipelineCreateInfo.renderPass = renderpass.get();
pipelineCreateInfo.subpass = 0;
pipelineCreateInfo.stageCount = 2;
pipelineCreateInfo.pStages = shaderStage;
vk::UniquePipeline pipeline = device->createGraphicsPipelineUnique(nullptr, pipelineCreateInfo).value;
vk::UniqueSwapchainKHR swapchain;
std::vector<vk::Image> swapchainImages;
std::vector<vk::UniqueImageView> swapchainImageViews;
std::vector<vk::UniqueFramebuffer> swapchainFramebufs;
auto recreateSwapchain = [&]() {
swapchainFramebufs.clear();
swapchainImageViews.clear();
swapchainImages.clear();
swapchain.reset();
vk::SurfaceCapabilitiesKHR surfaceCapabilities = physicalDevice.getSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(surface.get());
vk::SwapchainCreateInfoKHR swapchainCreateInfo;
swapchainCreateInfo.surface = surface.get();
swapchainCreateInfo.minImageCount = surfaceCapabilities.minImageCount + 1;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageFormat = swapchainFormat.format;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageColorSpace = swapchainFormat.colorSpace;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageExtent = surfaceCapabilities.currentExtent;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageArrayLayers = 1;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageUsage = vk::ImageUsageFlagBits::eColorAttachment;
swapchainCreateInfo.imageSharingMode = vk::SharingMode::eExclusive;
swapchainCreateInfo.preTransform = surfaceCapabilities.currentTransform;
swapchainCreateInfo.presentMode = swapchainPresentMode;
swapchainCreateInfo.clipped = VK_TRUE;
swapchain = device->createSwapchainKHRUnique(swapchainCreateInfo);
swapchainImages = device->getSwapchainImagesKHR(swapchain.get());
swapchainImageViews.resize(swapchainImages.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < swapchainImages.size(); i++) {
vk::ImageViewCreateInfo imgViewCreateInfo;
imgViewCreateInfo.image = swapchainImages[i];
imgViewCreateInfo.viewType = vk::ImageViewType::e2D;
imgViewCreateInfo.format = swapchainFormat.format;
imgViewCreateInfo.components.r = vk::ComponentSwizzle::eIdentity;
imgViewCreateInfo.components.g = vk::ComponentSwizzle::eIdentity;
imgViewCreateInfo.components.b = vk::ComponentSwizzle::eIdentity;
imgViewCreateInfo.components.a = vk::ComponentSwizzle::eIdentity;
imgViewCreateInfo.subresourceRange.aspectMask = vk::ImageAspectFlagBits::eColor;
imgViewCreateInfo.subresourceRange.baseMipLevel = 0;
imgViewCreateInfo.subresourceRange.levelCount = 1;
imgViewCreateInfo.subresourceRange.baseArrayLayer = 0;
imgViewCreateInfo.subresourceRange.layerCount = 1;
swapchainImageViews[i] = device->createImageViewUnique(imgViewCreateInfo);
}
swapchainFramebufs.resize(swapchainImages.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < swapchainImages.size(); i++) {
vk::ImageView frameBufAttachments[1];
frameBufAttachments[0] = swapchainImageViews[i].get();
vk::FramebufferCreateInfo frameBufCreateInfo;
frameBufCreateInfo.width = surfaceCapabilities.currentExtent.width;
frameBufCreateInfo.height = surfaceCapabilities.currentExtent.height;
frameBufCreateInfo.layers = 1;
frameBufCreateInfo.renderPass = renderpass.get();
frameBufCreateInfo.attachmentCount = 1;
frameBufCreateInfo.pAttachments = frameBufAttachments;
swapchainFramebufs[i] = device->createFramebufferUnique(frameBufCreateInfo);
}
};
recreateSwapchain();
vk::CommandPoolCreateInfo cmdPoolCreateInfo;
cmdPoolCreateInfo.queueFamilyIndex = graphicsQueueFamilyIndex;
cmdPoolCreateInfo.flags = vk::CommandPoolCreateFlagBits::eResetCommandBuffer;
vk::UniqueCommandPool cmdPool = device->createCommandPoolUnique(cmdPoolCreateInfo);
vk::CommandBufferAllocateInfo cmdBufAllocInfo;
cmdBufAllocInfo.commandPool = cmdPool.get();
cmdBufAllocInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
cmdBufAllocInfo.level = vk::CommandBufferLevel::ePrimary;
std::vector<vk::UniqueCommandBuffer> cmdBufs = device->allocateCommandBuffersUnique(cmdBufAllocInfo);
vk::SemaphoreCreateInfo semaphoreCreateInfo;
vk::UniqueSemaphore swapchainImgSemaphore, imgRenderedSemaphore;
swapchainImgSemaphore = device->createSemaphoreUnique(semaphoreCreateInfo);
imgRenderedSemaphore = device->createSemaphoreUnique(semaphoreCreateInfo);
vk::FenceCreateInfo fenceCreateInfo;
fenceCreateInfo.flags = vk::FenceCreateFlagBits::eSignaled;
vk::UniqueFence imgRenderedFence = device->createFenceUnique(fenceCreateInfo);
float time = 0;
auto old = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window)) {
glfwPollEvents();
device->waitForFences({imgRenderedFence.get()}, VK_TRUE, UINT64_MAX);
vk::ResultValue acquireImgResult = device->acquireNextImageKHR(swapchain.get(), 1'000'000'000, swapchainImgSemaphore.get());
if (acquireImgResult.result == vk::Result::eSuboptimalKHR || acquireImgResult.result == vk::Result::eErrorOutOfDateKHR) {
std::cerr << "スワップチェーンを再作成します。" << std::endl;
recreateSwapchain();
continue;
}
if (acquireImgResult.result != vk::Result::eSuccess) {
std::cerr << "次フレームの取得に失敗しました。" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
device->resetFences({imgRenderedFence.get()});
{
static std::chrono::system_clock::time_point prevTime;
static float rotation = 0.5f;
const auto nowTime = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
const auto delta = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(nowTime - prevTime).count();
rotation += delta * 2 * 3.14f / 1000000;
rotation = fmod(rotation, 2 * 3.14159f);
prevTime = nowTime;
auto model = translationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}) * rotationMatrix({0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f}, rotation) * scaleMatrix(1.0f);
auto view = viewMatrix({0.0f, -2.0f, -2.0f}, {0.0f, +0.707f, +0.707f}, {0.0f, +0.707f, -0.707f});
auto proj = projectionMatrix(3.14f / 3, float(screenHeight) / float(screenWidth), 0.1f, 100.0f);
sceneData.mvpMatrix = proj * view * model;
}
uint32_t imgIndex = acquireImgResult.value;
cmdBufs[0]->reset();
vk::CommandBufferBeginInfo cmdBeginInfo;
cmdBufs[0]->begin(cmdBeginInfo);
vk::ClearValue clearVal[1];
clearVal[0].color.float32[0] = 0.0f;
clearVal[0].color.float32[1] = 0.0f;
clearVal[0].color.float32[2] = 0.0f;
clearVal[0].color.float32[3] = 1.0f;
vk::RenderPassBeginInfo renderpassBeginInfo;
renderpassBeginInfo.renderPass = renderpass.get();
renderpassBeginInfo.framebuffer = swapchainFramebufs[imgIndex].get();
renderpassBeginInfo.renderArea = vk::Rect2D({0, 0}, {screenWidth, screenHeight});
renderpassBeginInfo.clearValueCount = 1;
renderpassBeginInfo.pClearValues = clearVal;
cmdBufs[0]->beginRenderPass(renderpassBeginInfo, vk::SubpassContents::eInline);
cmdBufs[0]->bindPipeline(vk::PipelineBindPoint::eGraphics, pipeline.get());
cmdBufs[0]->bindVertexBuffers(0, {vertexBuf.get()}, {0});
cmdBufs[0]->bindIndexBuffer(indexBuf.get(), 0, vk::IndexType::eUint16);
cmdBufs[0]->pushConstants(pipelineLayout.get(), vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eVertex, 0, sizeof(SceneData), &sceneData);
cmdBufs[0]->drawIndexed(indices.size(), 1, 0, 0, 0);
cmdBufs[0]->endRenderPass();
cmdBufs[0]->end();
vk::CommandBuffer submitCmdBuf[1] = {cmdBufs[0].get()};
vk::SubmitInfo submitInfo;
submitInfo.commandBufferCount = 1;
submitInfo.pCommandBuffers = submitCmdBuf;
vk::Semaphore renderwaitSemaphores[] = {swapchainImgSemaphore.get()};
vk::PipelineStageFlags renderwaitStages[] = {vk::PipelineStageFlagBits::eColorAttachmentOutput};
submitInfo.waitSemaphoreCount = 1;
submitInfo.pWaitSemaphores = renderwaitSemaphores;
submitInfo.pWaitDstStageMask = renderwaitStages;
vk::Semaphore renderSignalSemaphores[] = {imgRenderedSemaphore.get()};
submitInfo.signalSemaphoreCount = 1;
submitInfo.pSignalSemaphores = renderSignalSemaphores;
graphicsQueue.submit({submitInfo}, imgRenderedFence.get());
vk::PresentInfoKHR presentInfo;
auto presentSwapchains = {swapchain.get()};
auto imgIndices = {imgIndex};
presentInfo.swapchainCount = presentSwapchains.size();
presentInfo.pSwapchains = presentSwapchains.begin();
presentInfo.pImageIndices = imgIndices.begin();
vk::Semaphore presenWaitSemaphores[] = {imgRenderedSemaphore.get()};
presentInfo.waitSemaphoreCount = 1;
presentInfo.pWaitSemaphores = presenWaitSemaphores;
graphicsQueue.presentKHR(presentInfo);
}
graphicsQueue.waitIdle();
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
#version 450
#extension GL_ARB_separate_shader_objects : enable
layout(push_constant) uniform SceneData {
mat4 mvpMatrix;
} drawInfo;
layout(location = 0) in vec3 inPos;
layout(location = 1) in vec3 inColor;
layout(location = 0) out vec3 fragmentColor;
void main() {
gl_Position = drawInfo.mvpMatrix * vec4(inPos, 1.0);
fragmentColor = inColor;
}
#version 450
#extension GL_ARB_separate_shader_objects : enable
layout(location = 0) in vec3 fragmentColor;
layout(location = 0) out vec4 outColor;
void main() {
outColor = vec4(fragmentColor, 1.0);
}
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22)
project(vulkan-test)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
add_executable(app main.cpp)
find_package(Vulkan REQUIRED)
target_include_directories(app PRIVATE ${Vulkan_INCLUDE_DIRS})
target_link_libraries(app PRIVATE ${Vulkan_LIBRARIES})
find_package(glfw3 CONFIG REQUIRED)
target_link_libraries(app PRIVATE glfw)
最終更新: